Rosacea & Redness
Personalized protocols to reduce redness, calm inflammation, and restore skin balance
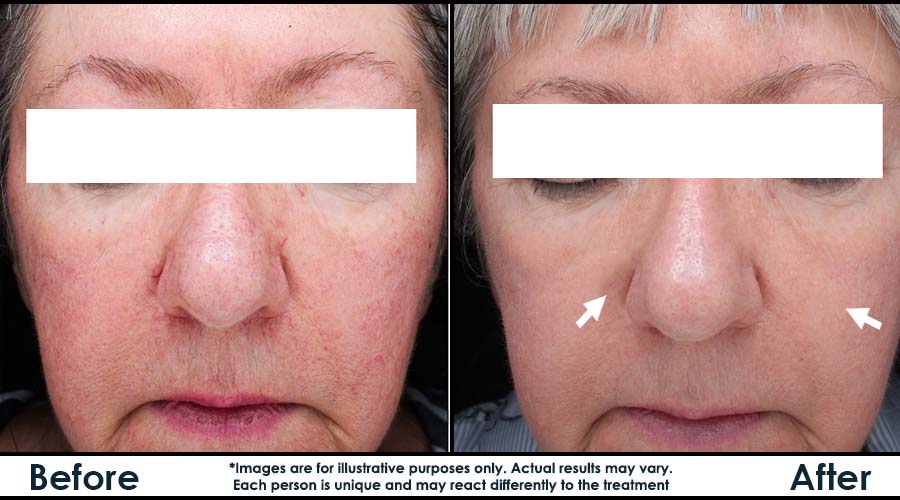
Before & After – Rosacea and Redness Treatment
Our Personalized Approach to Redness and Rosacea Treatment
1
In-depth consultation with advanced imaging to assess and identify the underlying causes of redness and rosacea
2
Effective treatment plan tailored to the severity and type of couperose or rosacea
3
Start of Treatment & Follow-Up to ensure progress
What Causes Facial Redness and Rosacea?
Have you noticed persistent facial redness, visible small blood vessels, or sudden skin flushing? Do you experience increased sensitivity or symptoms resembling rosacea? You may wonder: is it just a few dilated vessels—or something more? To better understand the difference, let’s take a closer look at how the skin works and what causes these reactions.
The Skin’s Structure and Its Role in Redness
The epidermis, the skin’s outermost layer, acts as a barrier to protect the body from external aggressors. It’s composed mainly of keratinocytes, which divide in the deeper layers and rise toward the surface, where they flatten and die to form a compact shield. This regeneration cycle takes about 28 days. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 0.05 mm to 0.1 mm.
Since this outer layer is made up of dead cells, it can become dry and flaky. To prevent this, the skin produces a hydrolipidic film—a mixture of sweat and sebum—that keeps the surface hydrated and protected. The epidermis has no blood vessels; instead, its cells are nourished by diffusion from the dermis. The blood vessels in the dermis are responsible for carrying nutrients and oxygen to the skin’s surface, which also plays a role in redness.
This close relationship between the dermis and epidermis explains why any disturbance in the blood vessels—such as dilation, inflammation, or increased flow can visibly affect the skin’s surface, especially in sensitive individuals. When blood vessels become more reactive or remain dilated for prolonged periods, they can lead to persistent redness, flushing, or the appearance of visible capillaries (telangiectasias). Over time, these vascular changes may evolve into rosacea, a chronic condition that requires a personalized, medical-grade approach to prevent progression and manage symptoms effectively.
What Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic, progressive skin condition that develops in four clinical stages:
- Stage 1 – Flushing: Sudden facial redness triggered by emotions, spicy foods, or temperature changes. The skin returns to normal after a short time.
- Stage 2 – Early Rosacea (Erythrosis): Persistent mild redness, often with small, visible blood vessels (telangiectasias).
- Stage 3 – Papulopustular Rosacea: More pronounced redness accompanied by red bumps or pustules, which may resemble acne.
- Stage 4 – Rhinophyma (Advanced Stage): Typically affects men; often linked to excess alcohol, this stage involves thickened skin, especially around the nose, which becomes bulbous, red, and enlarged.
Main Causes of Redness and Rosacea
Several factors can contribute to the appearance or worsening of facial redness and rosacea:
- Thin epidermal barrier: Makes underlying blood vessels more visible.
- Deficient hydrolipid film: Causes skin to lose its protective power; the body increases blood flow to the surface to compensate, resulting in redness and sensitivity.
- Vascular hyperactivity: An overactive blood vessel network can trigger persistent flushing and inflammation.
- Immune system imbalance: Can lead to repeated vasodilation and inflammatory breakouts.
- Neurovascular disorders: Cause uncontrolled blood flushes, which contribute to the formation of telangiectasias and bumps.
- Environmental triggers: Sun, wind, heat, cold, alcohol, spicy food, mites, or harsh skincare products may worsen rosacea symptoms.
- Chronic nature: Rosacea cannot be permanently cured, but it can be effectively controlled. Once optimal results are achieved, maintenance treatments are recommended yearly to prevent recurrence.
Redness and Rosacea
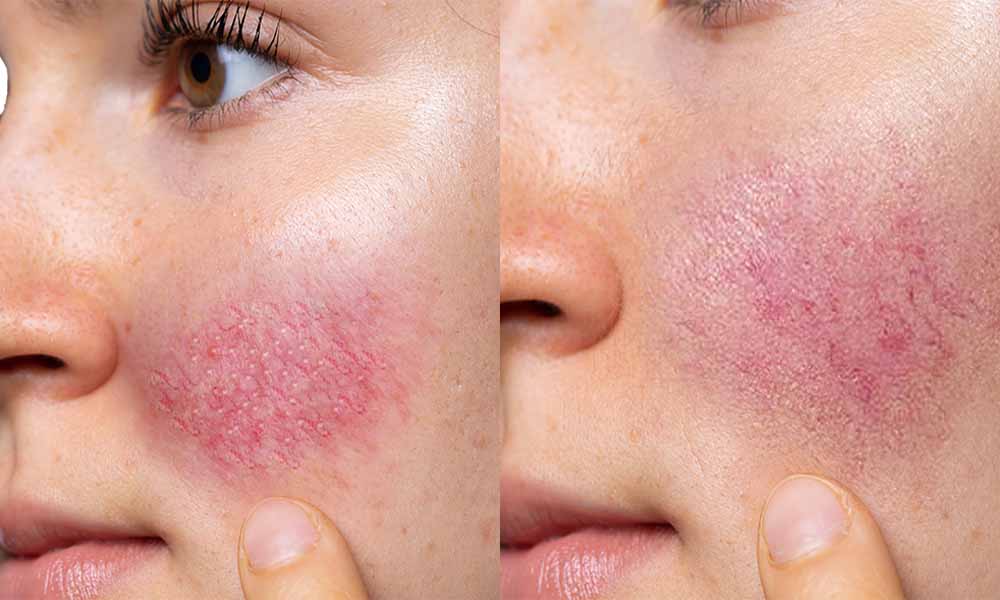
Our Approach to Treating Redness and Rosacea
First, it is important to return to the origin — the initial appearance of facial redness or pimples associated with rosacea. During your consultation, we’ll ask targeted questions to better understand your symptoms, triggers, and progression of the condition.
Then, using advanced 3D imaging, we will analyze the internal network of blood vessels within your skin. This step is essential, as it helps us identify areas of vascular congestion, inflammation, and capillary damage. It also reveals the depth and distribution of the affected vessels — allowing for precise and personalized treatment planning.
We will also assess whether your epidermal barrier is functioning properly. Many individuals suffering from rosacea have fragile skin, increased sensitivity in the cheeks, and visible dryness — all signs of a weakened hydrolipidic barrier.
Because every skin is different, the treatment plan is tailored to your skin’s needs, based on the analysis performed during consultation. Here are some examples of therapeutic options that may be used individually or in combination:
- Application of topical creams at home to restore the skin barrier and reduce inflammation.
- Oral or topical antibiotics, in cases where inflammatory pustules are present.
- Laser, Deep Vascular, BBL (BroadBand Light) or intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments to reduce visible blood vessels and control chronic redness.
- Cauterization (thermocoagulation) for treating fine or stubborn capillaries that do not respond to light-based therapies.
- Sclerotherapy injections, for larger individual vessels that cannot be treated with light-based devices.
- Collagen stimulation therapies, to thicken thin, fragile skin and improve vascular permeability.
- Cooling treatments or anti-inflammatory protocols, in acute flare-ups or post-procedure care.
This multi-step approach allows us to treat both the visible symptoms and the underlying causes, helping to restore skin comfort, clarity, and balance. Long-term management may include maintenance treatments twice a year to prevent recurrence.



